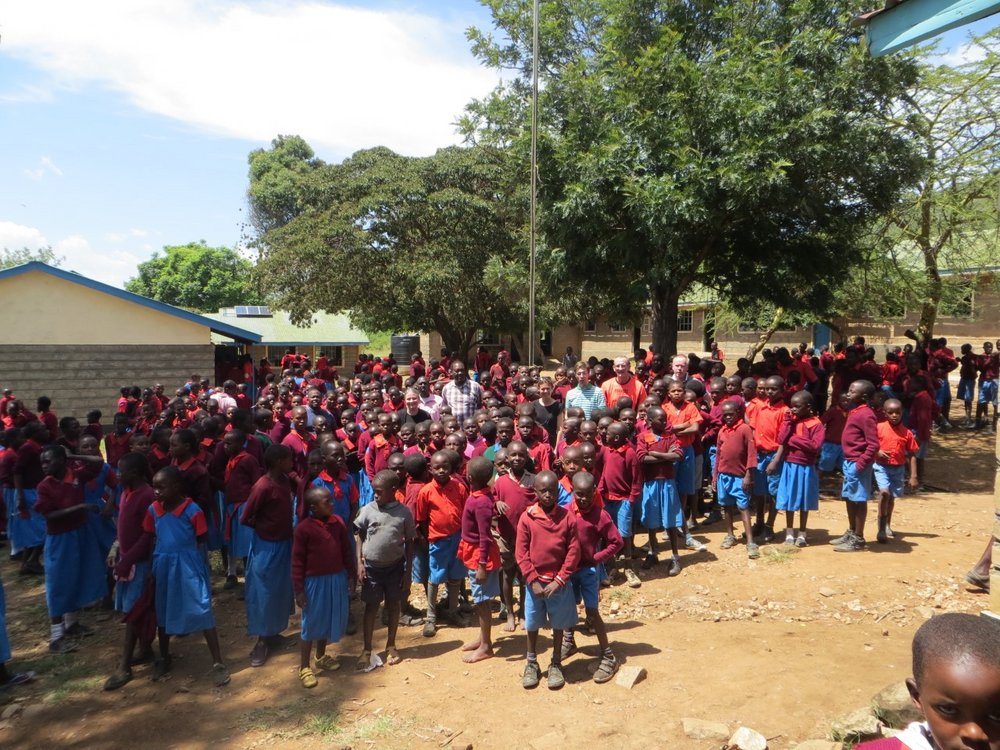
The highly leukotoxic JP2 genotype of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans has been detected in Maasai Mara, Kenya.
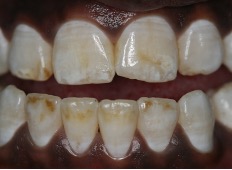
In the recent paper by Haubek and coworkers (2021), published in the MDPI journal, Pathogens, it was reported that among 284 Kenyan adolescents from Narok County, Mara North Conservancy, Maasai Mara, who were clinically examined and microbiologically sampled for a well-known and geographically widespread occurring highly leukotoxic variant of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans (Aa), termed the JP2 genotype, were found to have this microorganism.
The presence of the JP2 genotype of Aa is associated with development of periodontitis, a gum disease that eventually may lead to loosening and loss of teeth. However, the prevalence of the JP2 genotype of Aa found among the youth in Mara North Conservancy was found to be relatively low compared to the findings in studies carried out in, for example, North- and West-African countries.
The geographic dissemination of the highly leukotoxic JP2 genotype of Aa is of particular interest due to its high pathogenic potential. It has previously been reported that the JP2 genotype of Aa is likely to be an important etiological agent in the initiation of periodontal attachment loss in adolescents. The JP2 genotype is characterized by a 530-bp deletion in the promoter region of the leukotoxin gene operon, which results in enhanced production of the exotoxin, leukotoxin that is able to kill important cells of the immune system and cause inflammation.
What to look for as warning signs of the development of gingivitis and periodontitis:
- Gums that bleed during brushing
- Dental plaque accumulating along the gum line
- Accumulation of bacteria/plaque that harden (tarter or calculus) and stay on the tooth surface and within the periodontal pockets around the teeth
- Red, swollen and sore gums
- Gums that have pulled away from the tooth crowns and leave bare tooth roots
- Teeth becoming increasingly loose
- Persistent bad breath
Prevention:
- You can contribute to the prevention of periodontitis by brushing twice a day, cleaning between teeth once a day with dental floss, and visit a dentist once a year, whenever possible.
The research project, led by professor Dorte Haubek, was carried out by a group of researchers from the University of Aarhus, Denmark, the University of Umeaa, Sweden, and the University of Nairobi, Kenya, and ethically approved by the KNH–UoN Ethics and Research Committee, Kenya (P711/11/2015, 25 January 2016).
The International publication, which is now published in the international journal, Pathogens, can be found via the link below:
https://www.mdpi.com/2076-0817/10/4/488
Read the article in Swahili here: https://mgmt.au.dk/maasaimarascience/research/oral-diseases-and-infant-oral-mutilation-in-the-population-of-masai-mara/aina-ya-kimaumbile-ya-leukotoxic-jp2-ya-aggregatibacter-actinomycetemcomitans-imegunduliwa-katika-maasai-mara-kenya/
